Blockchain technology has unlocked a new era in finance by introducing digital asset tokens. Among these, security tokens and utility tokens are two of the most discussed categories. For investors, developers, and financial professionals alike, understanding the nuances between these token types is essential. In this detailed guide, we explore the security token vs utility token debate, define each token type, compare their features, and answer common queries all while examining how they fit into the broader landscape of token classification and digital asset management.
Introduction
The rapid evolution of blockchain has led to the emergence of various digital asset tokens. As the market grows, so does the need for clarity around key concepts like security token definition and utility token definition. This article will cover:
- What is a Security Token?
- What is a Utility Token?
- Advantage and Disadvantage of Security Tokens
- Advantage and Disadvantage of Utility Tokens
- A side-by-side blockchain token comparison
- The role of regulatory tokens and investment tokens
- Key token standards such as ERC-20 and ERC-1400
- Frequently asked questions and common user queries
By understanding the crypto token differences between security tokens and utility tokens, you can make informed decisions whether you’re investing, developing a blockchain application, or navigating the evolving landscape of digital finance.
What is a Security Token?
A security token is a digital representation of ownership in an underlying asset. These tokens are issued on a blockchain and are designed to mirror traditional securities like stocks, bonds, or investment funds. They come with specific legal rights such as dividend distributions, voting rights, or profit-sharing mechanisms.
Key Attributes of Security Tokens:
-
Investment Focus: Security tokens are meant for investment, offering the same benefits as traditional securities. They often function as investment tokens, providing dividends, equity, or profit sharing.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Being regulatory tokens, security tokens must comply with financial regulations, including securities laws, investor protection standards, and rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes.
-
Token Standards: They often adhere to standards like ERC-1400, which is specifically designed for security tokens, ensuring legal and operational compliance.
Understanding the security token definition is crucial for investors seeking assets that offer legal safeguards and potential financial returns.
What is a Utility Token?
In contrast, a utility token is designed to provide access to a product or service within a blockchain ecosystem rather than representing an ownership stake. Utility tokens are not primarily used as investments; their value lies in the functionality they offer to users.
Key Attributes of Utility Tokens:
-
Access & Functionality: These tokens serve as the “fuel” of a platform, allowing users to access various services, participate in network operations, or pay for transaction fees. They are often the lifeblood of decentralized applications (dApps).
-
Lower Regulatory Burden: Utility tokens typically face fewer regulatory requirements compared to security tokens. Their use is primarily for facilitating ecosystem functionalities rather than providing investor returns.
-
Token Standards: Utility tokens are usually built on standards like ERC-20, which enables widespread adoption, interoperability, and liquidity within decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
The utility token definition highlights their role in enabling platform access, making them essential for projects that focus on user engagement and service utilization rather than direct profit distribution.
Advantage and Disadvantage of Security Tokens
Pros
-
Investor Rights: Security tokens offer features akin to traditional securities, such as dividends, profit sharing, and voting rights. This means investors can directly benefit from the financial performance of the underlying asset, much like owning stocks or bonds in a conventional market.
-
Regulatory Compliance: These tokens are designed to meet stringent regulatory standards, which enhances investor protection. They comply with securities laws and other legal requirements (such as KYC and AML), fostering trust among institutional and individual investors. This adherence to regulations not only legitimizes the tokens but also reduces the risk of fraud.
-
Structured Investment: Security tokens provide a clear, well-defined framework for ownership and capital appreciation. Investors can easily understand their stake in an asset, making it easier to assess risks and potential returns. This structure mimics traditional investment vehicles, offering predictability and clarity in a digital format.
Cons
-
Complex Regulations: The stringent regulatory environment means security tokens face complex legal and compliance requirements. This complexity can lead to delays in token issuance and limit trading flexibility, as every transaction might need to adhere to strict regulatory oversight.
-
Limited Flexibility: Since they are primarily designed as investment vehicles, security tokens are less adaptable for other purposes. Their functionality is largely confined to financial returns and ownership rights, which restricts their use in broader applications such as accessing digital services or participating in decentralized networks.
-
Higher Costs: The process of ensuring regulatory compliance, including legal audits, certification, and ongoing monitoring, incurs significant costs. These higher expenses can affect both the initial issuance and subsequent trading, making security tokens more expensive to manage compared to less regulated token types.

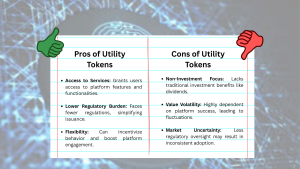
Advantage and Disadvantage of Utility Tokens
Pros
-
Access to Services: Utility tokens are engineered to provide access to specific products or services within a blockchain ecosystem. They act as a “key” that unlocks various features of a platform, encouraging user engagement and participation in decentralized applications (dApps).
-
Lower Regulatory Burden: Unlike security tokens, utility tokens are generally not intended as investment vehicles and thus face fewer regulatory hurdles. This lighter regulatory framework allows for a faster, more straightforward issuance process, reducing the administrative and legal overhead.
-
Flexibility: Utility tokens are versatile and can be programmed to serve multiple functions, such as incentivizing users, facilitating transactions, or even participating in governance mechanisms within a platform. This adaptability makes them ideal for projects aiming to foster active user communities and enhance platform growth.
Cons
-
Non-Investment Focus: The primary purpose of utility tokens is to enable access and functionality, not to provide direct financial returns. As a result, they typically do not offer benefits like profit sharing or dividends, which may limit their appeal to traditional investors seeking income-generating assets.
-
Value Volatility: The value of utility tokens is closely linked to the performance and adoption of the platform they serve. If the platform struggles to gain traction, the token’s value can fluctuate wildly, creating a higher risk profile for holders.
-
Market Uncertainty: Given their focus on functionality over investment, utility tokens may experience market uncertainty and inconsistent adoption. The lack of a robust regulatory framework can lead to unpredictable market behavior, making it challenging for token issuers and users to establish long-term stability.
Security Token vs Utility Token: A Side-by-Side Comparison
This comparison highlights key differences: Security tokens represent ownership, offer investment benefits, and follow strict regulations (e.g., ERC-1400, STOs). Utility tokens provide access to services, face minimal regulation (e.g., ERC-20), and are commonly used in dApps and ICOs.
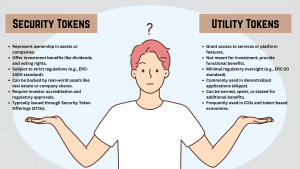
This blockchain token comparison clearly shows that while both tokens are essential in the digital ecosystem, they serve very different purposes.
Regulatory Tokens and Token Standards
Security tokens, as regulatory tokens, require adherence to strict regulatory frameworks to ensure investor protection. They benefit from robust compliance structures that make them similar to traditional financial instruments. On the other hand, utility tokens prioritize functionality and user engagement.
Token Standards:
-
ERC-20: Widely used for utility tokens, enabling standardization and ease of integration across various DeFi applications.
-
ERC-1400: Designed for security tokens, this standard incorporates features that facilitate regulatory compliance and investor rights.
Understanding these standards is crucial when evaluating digital asset tokens and their place in your investment strategy or blockchain project.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a security token and a utility token?
- Security tokens represent investment interests with legal rights, whereas utility tokens provide access to a platform’s services.
How do security tokens differ from utility tokens?
- Security tokens are regulated and offer profit-sharing, while utility tokens focus on functionality without being designed as investment vehicles.
Which is better: security tokens or utility tokens?
- It depends on your objectives: choose security tokens for regulated investments and utility tokens for accessing blockchain services.
Are security tokens more regulated than utility tokens?
- Yes, security tokens must comply with rigorous securities regulations, unlike utility tokens which have a lighter regulatory burden.
How are security tokens used in investment compared to utility tokens?
- Security tokens are used like traditional securities, offering dividends and ownership rights. Utility tokens, however, are used within a platform to access features and services.
What are the benefits of security tokens over utility tokens?
- Security tokens provide regulated investment opportunities, legal protections, and potential income through dividends, while utility tokens drive platform usage and network effects.
Conclusion
The debate of security token vs utility token is central to understanding the digital asset landscape. By grasping the differences between these token types, you can make more informed decisions whether you’re investing in regulated securities or engaging with blockchain services.
For DeployTokens readers, this comprehensive guide highlights how proper token classification and adherence to token standards like ERC-20 and ERC-1400 can empower you in navigating the world of digital asset tokens. Whether you are considering a security token for its investment potential or a utility token for its functional benefits, the insights shared here will help you understand the crypto token differences and make strategic decisions in the evolving blockchain ecosystem.
Stay informed, evaluate your goals, and explore the dynamic opportunities that tokenization offers in reshaping finance and digital asset management.
